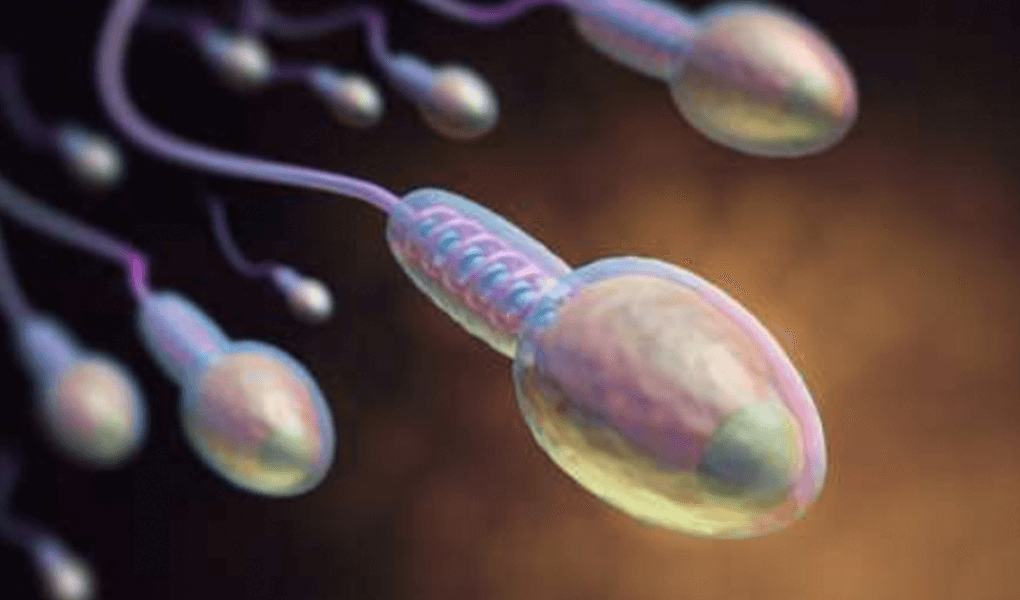
Semen analysis is one of the first requested tests among men who have infertility problems and apply to a specialist clinic to have children. The semen analysis involves a detailed examination of the sperm cells contained in the semen sample obtained from the male after 2-7 days of sexual abstinence in terms of number, mobility, and deformity.
For people whose sperm count, motility and morphology are below normal values, depending on their values, the time may take longer to have children in a natural way.
What is Sperm Morphology?
Sperm morphology and sperm deformities are examined. The most common assessment methods used for the determination of deformities in sperm in the world are the assessment methods performed according to the criteria of the World Health Organization (WHO) and Kruger.
In these methods, the sperm cells to be examined are subjected to special preparation processes and evaluated in detail in terms of different parts of the sperm (head, neck, and tail). As a result of the evaluation, results in which the proportion of sperm cells with normal standards are above a certain number are considered normal.
Importance of Sperm Morphology
In most clinics, sperm is only evaluated for motility and quantity. In fact, studies in recent years show sperm deformity is more important than motility and quantity. The reason is that sperm production is a process that lasts about seventy days and in this process, the quality control department does not work in a simple way. In other words, we consider this sample as normal sperm because four of the one hundred sperm produced have a normal shape.
If there is a problem in this process, it reflects as a deformity in sperm morphology. This means, if specific deformities observed in high percentages, before starting the IVF treatment, we can plan the treatment according to the major deformities. For example, we know that there will be a fertilization problem with glozozoospermia deformity, which is a given name to those sperms with a round head. We can take important extra cautions in our laboratories. Having short tail, head deformities, etc. It gives us an understanding of how to plan the treatment. Therefore, morphologic evaluation of the treatment and tests are highly important.
How should sperm morphology be?
The sperm cell consists of three parts. These; head part, middle and tail part. The head contains genetic material, the middle part provides the energy needed for the sperm to move and the tail part provides the sperm movement.
Head length of a normal sperm: 4 to 5 µm
Head section width: 2.5 – 3.5 µm
The length/width ratio of the head should be 1.50 – 1.75.
The tail section is thinner than the middle and is curved, well-formed sperm approximately have 40-50 µm long.
Sperm Deformity Treatment
One of the questions frequently asked by the patients is “how does sperm morphology can improve?”. It is difficult to say that we can correct deformities in the sperm. Our knowledge about which hereditary and external factors can cause deformities in sperm is extremely limited during a period of about 3 months starting from the stem cell to the mature sperm stage. While it is not possible to improve this problem when it is inherited, there are also conclusions that the deformities due to transient external factors can be improved after the elimination of these factors.
To date, there are no meaningful and acceptable conclusions that sperm shape disorders can be cured in studies involving vitamins and nutritional supplements for improvement. However, these treatments, especially in the head of the sperm in the genetic burden of damage to the results showing that the reduction is available. Therefore, in some patients, mentioned supportive treatments may contribute to the treatment as number, mobility, and quality of genetic structure rather than sperm deformities.







Be the first to comment