Follow Us!
Patient stories, informative videos and much more on our social media accounts
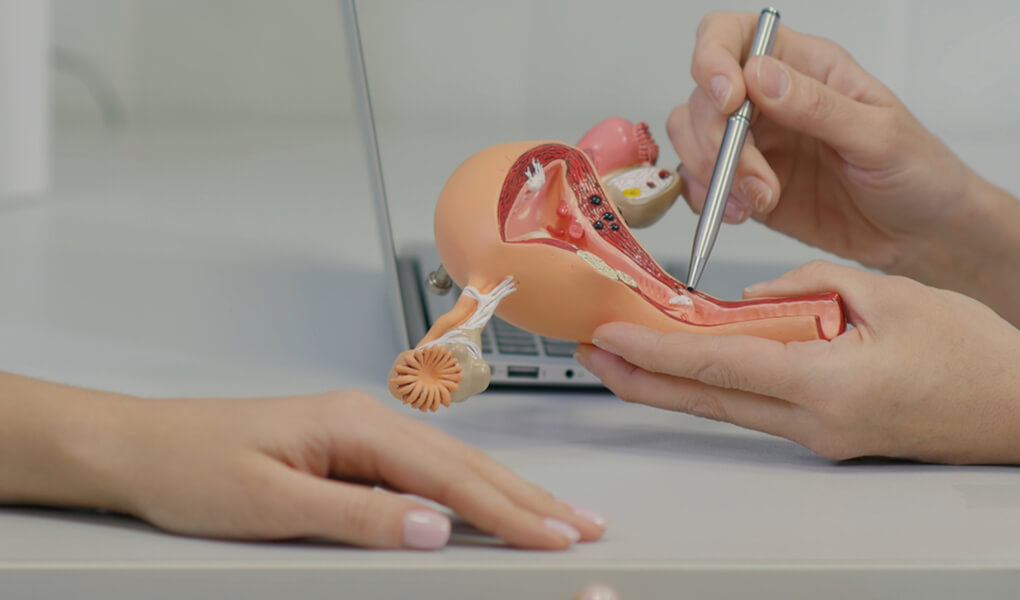
The question “what is a follicle cyst?” can be answered as a cyst that forms when an ovarian follicle fails to release an egg during ovulation. This process is closely linked to the menstrual cycle and hormone regulation.
During a normal cycle:
If the follicle does not rupture due to hormonal imbalance or excessive stimulation, fluid accumulates inside it and a cyst forms. Over time, this cyst may enlarge but often remains filled with clear fluid.
In medical literature, follicle cysts may also be referred to in different languages:
All of these terms describe the same benign condition.
Follicle cysts can develop in anyone who ovulates, but certain factors increase the likelihood of formation:
Functional cysts are less common in women who use birth control pills, as ovulation is suppressed. However, in rare cases, hormonal contraception may still be associated with cyst formation.
Follicle cysts are uncommon before puberty and after menopause, as ovulation does not occur regularly during these periods.
Most follicle cysts do not cause noticeable symptoms and are discovered incidentally during routine gynecological examinations.
However, larger cysts or those that rupture may lead to symptoms such as:
Many women ask whether a follicle cyst can delay menstruation. Since ovulation does not occur when a follicle cyst forms, temporary menstrual irregularities or delays may occur.
The location of the cyst—left or right ovary—does not significantly change symptoms, aside from the side where pain may be felt.
A common concern is “is follicular cyst dangerous?” In most cases, the answer is no. Follicle cysts are benign and non-cancerous.
However, complications may occur in rare situations:
Symptoms that may indicate a complication include:
These situations require immediate medical attention.
Many women wonder whether pregnancy is possible with a follicle cyst. In most cases, follicle cysts do not cause infertility. In fact, the presence of a functional cyst indicates that the hormonal mechanisms required for ovulation are active.
Large follicle cysts may temporarily interfere with blood flow to the ovaries or fallopian tubes, which can make conception more difficult. In such cases, surgical removal may be recommended.
After treatment, pregnancy may occur naturally. In women of advanced reproductive age, assisted reproductive techniques may be considered if pregnancy does not occur within several months.
If a follicle cyst ruptures, pain is often felt on the side of the affected ovary. Small cyst ruptures may go unnoticed, while larger cysts can cause significant internal bleeding.
Severe bleeding may lead to symptoms such as:
This is a medical emergency and requires immediate evaluation and treatment.
Most follicle cysts are detected during routine pelvic examinations or ultrasound scans. If symptoms are present, additional diagnostic tools may be used:
Symptoms of a ruptured follicle cyst can resemble appendicitis, making accurate diagnosis critical.
Treatment depends on cyst size, symptoms, age, and reproductive status.
Surgical treatment is usually minimally invasive and allows for quick recovery. Follicle cysts do not cause cancer and are generally not considered dangerous.
It is a benign ovarian cyst that forms when a follicle does not release an egg during ovulation.
A follicle cyst itself is not pregnancy, but pregnancy can occur alongside a functional cyst.
“Quiste folicular” is the Spanish term for follicle cyst.
Yes, most follicle cysts resolve naturally within a few menstrual cycles.
No, follicle cysts are benign and non-cancerous.
You can reach us at 444 39 49 for all your questions about the diagnosis, treatment and other issues of follicle cysts.
Let us call you as soon as possible regarding the issues you want to consult.