Follow Us!
Patient stories, informative videos and much more on our social media accounts
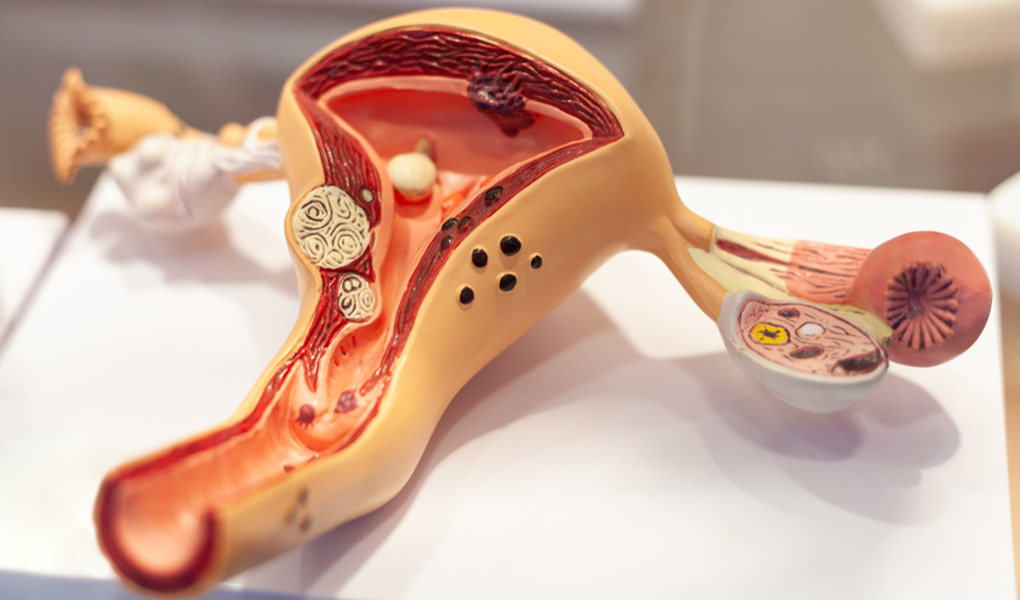
World Health Organisation (WHO) data shows today, every 6th person loses their life due to cancer. Cervical (uterine) cancer is one of the most common female cancer and in Turkey is the 4th most common female cancer. Cervical cancer is evaluated under 2 sub-headings those are; spread in the uterus and roots from the mucosa in the uterine that is called endometrium, and roots from the muscle layer of uterine that is called myometrium. The type that roots from the muscle later are called “sarcoma”. Sarcoma are seen less frequently; they are more aggressive type and generally treatment is harder. Type that roots in the endometrium, carcinomas that is also known as endometrial cancer, is generally observed after menopause. It is possible to fully recover from this with early diagnoses.
The endometrium is the layer where the fertilized egg is implanted, and baby develops here. Women in reproductive age, oestrogen and progesterone hormones secreted from the ovaries play a role in coordinating the preparation and thickening of the endometrium for pregnancy and shedding if pregnancy is not formed. This layer proliferates every month until the woman enters menopause and prepares for a possible pregnancy. If the pregnancy is not formed, it is removed from the body by menstrual bleeding. However, sometimes endometrial cells proliferate uncontrolled to form tumours. If left untreated, cancer cells may spread to different layers of the uterus first, then to neighbouring organs such as the ovaries, and later to distant organs such as the lung. (metastasis).
The cause of uncontrolled proliferation of endometrial cells is unknown. It is thought that disruption of oestrogen-progesterone balance in favour of oestrogen may lead to endometrial cancer. That is, longer and higher exposure to oestrogen, progesterone-free hormone replacement therapies containing only oestrogen may pave the way.
Especially post-menopause vaginal bleeding is the most common symptom. During this period all types of bleedings are abnormal and require medical support. For the women in reproduction period, most important 2 symptoms are; having vaginal bleeding between two periods and pain below belly, unexplained weight lost. Depending on the stage and spread area, those symptoms can show differences.
Risk factors pave the way for the endometrium cancer however we cannot generalize by saying these risk factors will have cancer.
Age: Majority of the patients diagnosed are above 55. Number of diagnosed patients increase with the age.
Obesity: Presence of obesity may increase the risk of endometrium cancer by 2-4 times.
Early Menstrual Cycle: People who start their menstruation before 12 years old, has been exposed to estrogen for many years.
Having Oestrogen Treatment: Drug treatments that do not contain progesterone, which are estrogen stabilizers.
Late Menopause: Women who enter menopause after 50 years old, are exposed to oestrogen for many years.
PCO (Polcystic Ovary Syndrome)
Cancer History in the Family: Having cancer story in at least 1 of those three; parents, siblings or children
Ovarian Tumours: Some types cause production of oestrogen in the body, therefore causes having high levels of oestrogen.
Use of tamoxifen for cancer treatment
Infertility or not given birth before
Diabetes
Hypertension
If you have any of the symptoms stated above, you should visit your doctor urgently. Endometrium cancer can be treatment if diagnosed in early stages.
With ultrasound, thickness and structure of the endometrium can be observed. If there is a suspicious condition is seen, for definite diagnoses endometrial biopsy is taken. During the biopsy, with a thin tube sample of mucosa is taken. If the sample taken is not enough, with either dilatation or curettage methods samples are taken from the mucosa, those are performed under anaesthesia in operation room conditions. Samples are taken from all the uterus walls and sent for pathological investigation. Definite diagnoses are placed after the detailed examination under microscope. If the presence of the disease is verified to be able to determine the stage of the disease further examinations are requested from your doctor.
Endometrium cancer stages are;
1st Stage: Limited only in uterus.
2nd Stage: Spread into the cervix.
3rd Stage: It has spread to fallopian tubes, ovaries, vagina or lymph nodes.
4th Stage: It has spread to proximal organs such as the bladder or colon, or to the upper abdomen, lung or groin lymph nodes.
Treatment options are depending on many different factors. Stage of the disease, age of the patient, accompanying medical conditions with the disease, desire to have a child such conditions affect the treatment protocol. Specifically, one or more surgical, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and hormone therapy options are applied depending on the patient’s condition.
Surgery: It is the main treatment modality in endometrial cancers. The hysterectomy is the process of removing the cervix and cervix. This process is often involved in the removal of the ovaries. If necessary, during the procedure, the lymph nodes in the pelvis and abdomen can also be removed. Minimally invasive surgical methods such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery with a smaller incision can also be used. The tissues removed after surgery are subjected to pathological examination to determine the stage of the disease.
Radiotherapy: Your doctor may recommend radiotherapy if he thinks the disease will relapse based on the findings obtained after the surgical procedure. Radiotherapy is also beneficial in patients who are not suitable for surgical intervention.
Chemotherapy: It is a method in which cancer is treated with medication. Chemotherapy is usually applied in later stages (stage III and IV) or in cases where the disease recurs after the first treatment. Although the number of drugs to be used varies according to the condition of the patient and the disease, combinations of drugs are often used in this treatment method. Chemotherapy is not confined to a specific area, such as surgical treatment and radiotherapy, and drugs affect all cancer cells that have metastasized through the bloodstream.
Hormone Treatment: High doses of progesterone can be used to stop cancer cells spread to other parts of the body. If the size of the tumour is appropriate and it has been determined that it does not spread to the uterine wall, organ-preserving treatment can be applied instead of surgical procedure in patients who want to preserve their fertility. It is also possible to conceive by closely monitoring the patient’s response to high-dose progesterone.
Even though, it is not possible to protect yourself fully against endometrium cancer, it is possible to reduce the risk factors you carry. It is a known fact that, having fatty nutrition causes increase of oestrogen levels increase the risk of endometrium cancer. In Turkey, annually there are about 6000 endometrium cancer cases related with obesity. Cancers that are affect by obesity affects women more compared with men. For the cases where ovulation irregularities are present, oestrogen exposure increases the risk of endometrium cancer. Polycystic ovary syndrome causes ovulation irregularity and treatment of this is possible. With the PCO treatment you can lower the endometrium cancer risk. Having periodic gynaecologic examinations, having regular smear tests, if advised from your doctor you can get endometrium cancer vaccination, and self-checking for symptoms if necessary applying to your doctor, if you had endometrium cancer before continuing your regular examinations also decreases the risk of endometrium cancer.
You can get your examination booked from our specialist to get more information about endometrium and cervix cancer and the risks you have.
For all your questions you can call +90 444 39 49 to reach us.
Let us call you as soon as possible regarding the issues you want to consult.