Follow Us!
Patient stories, informative videos and much more on our social media accounts
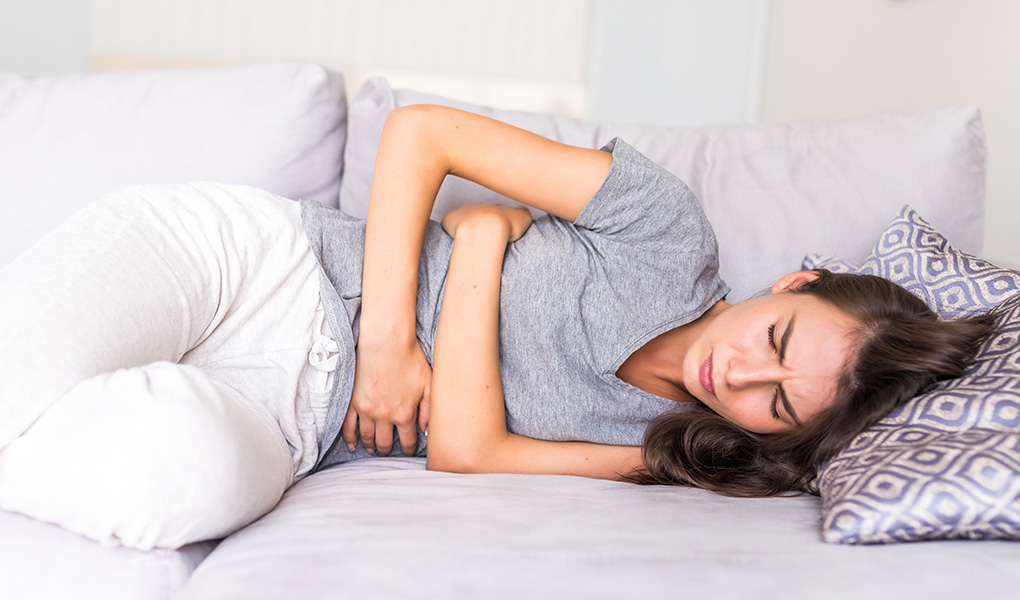

A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common health issue, especially among women. A simple urinary tract infection usually does not lead to serious problems. However, infections that affect the kidneys can cause severe complications.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection and What Causes It?
A urinary tract infection is a general term for infections that occur in the excretory system. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. An infection in any of these areas is called a urinary tract infection.
Bacterial infection is the most common cause of urinary tract infections. Less frequently, fungal and viral infections can also lead to a UTI.
Urinary tract infections can have specific names depending on the infected organ. These are:
Cystitis: This refers to an infection of the bladder. Patients with cystitis may experience symptoms such as a burning sensation and abdominal pain while urinating. It may also cause cloudy urine or blood in the urine.
Pyelonephritis: This is the term for an infection of the kidneys. Pyelonephritis can lead to symptoms such as fever, chills, and vomiting. It is a serious infection that can have severe consequences.
Urethritis: This is an infection of the urethra, which facilitates the elimination of urine from the body. Urethritis can cause a burning sensation during urination and discharge.
What Are the Symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection?
A urinary tract infection may not cause symptoms in some people. Additionally, the symptoms may vary depending on the type of urinary tract infection.
Symptoms caused by infections in the lower urinary tract, such as the urethra and bladder, include:
Infections in the upper urinary tract are more serious. Pyelonephritis, a kidney infection, can lead to a condition called urosepsis, where the bacteria causing the infection enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Urosepsis can cause serious problems, including low blood pressure, coma, and even death.
Symptoms of infections in the upper urinary tract include:
Can Cold Weather Cause a Urinary Tract Infection?
The risk of urinary tract infections increases when urine is not frequently voided and remains in the urinary tract for a prolonged period. In colder weather, people generally drink less liquid, which leads to less frequent urination. As a result, urinary tract infections are more common in winter.
Other risk factors for urinary tract infections include:
Female Anatomy: Women’s urethral openings are located very close to the anus, which hosts many bacteria. Additionally, the female urethra is shorter than the male urethra. Both factors contribute to bacteria entering the urinary tract, causing infections. Therefore, urinary tract infections are more common in women than in men.
Urinary Tract Anomalies: Infants born with structural differences, such as narrow urinary tracts or abnormalities that prevent urine from exiting the body, are at higher risk for infections.
Conditions That Block Urine Flow: Conditions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can interfere with urine flow and lead to infections.
Sexual Activity: Sexually active individuals have an increased risk of developing urinary tract infections.
Weakened Immune System: Diseases that suppress the immune system, such as diabetes, can also increase the risk of urinary tract infections.
Use of Catheters: People who are unable to urinate on their own may need a catheter inserted for urine drainage. The use of a catheter increases the risk of infections.
Where Does a Urinary Tract Infection Cause Pain?
Infections in the lower urinary tract, such as urethritis and cystitis, cause pain in the pelvic region in women. The pelvic area refers to the area below the abdomen and above the pubic bone. Women with lower urinary tract infections may experience tenderness and pain in this area. The same infection in men may cause rectal pain, or pain around the anus and rectum.
Infections in the upper urinary tract, such as pyelonephritis, cause pain in the kidney area. This pain is typically felt in the side or lower back. Side pain, also known as flank pain, is a common symptom. Upper urinary tract infections can also cause back and lower back pain.
Do Urinary Tract Infections Affect Sexual Activity in Men?
Urinary tract infections typically do not have a negative effect on sexual activity. However, if a urinary tract infection is caused by prostate enlargement, it can lead to a decrease in sexual function. Men with symptoms of a urinary tract infection should seek medical attention promptly for necessary tests.
Conditions such as prostate enlargement or kidney stones must be addressed before an infection can be successfully treated. Treating the infection without resolving these underlying issues will not be effective.
How is a Urinary Tract Infection Treated?
If a urinary tract infection is caused by conditions like kidney stones, urinary tract anomalies, or prostate enlargement, these conditions should be addressed first.
Since urinary tract infections are primarily caused by bacteria, antibiotics are used for treatment. In cases of simple infections, a specific antibiotic is prescribed based on the urine culture results. For more severe cases, patients may be hospitalized and treated with intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
What Helps Relieve a Urinary Tract Infection?
There are various remedies that can help speed up the recovery from a urinary tract infection. One of the most important is drinking plenty of fluids. Hydration, especially with water, dilutes the urine and helps flush bacteria from the body before they can multiply. It is important to avoid beverages that may irritate the bladder, such as coffee, alcohol, and citrus juices, until the infection is gone.
Let us call you as soon as possible regarding the issues you want to consult.