Follow Us!
Patient stories, informative videos and much more on our social media accounts
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver and can lead to both acute and chronic disease. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) is transmitted through blood, sexual contact, contaminated medical equipment, and from mother to baby during pregnancy. While some individuals experience flu-like symptoms after infection, many people may carry the virus without noticeable signs for months or even years.
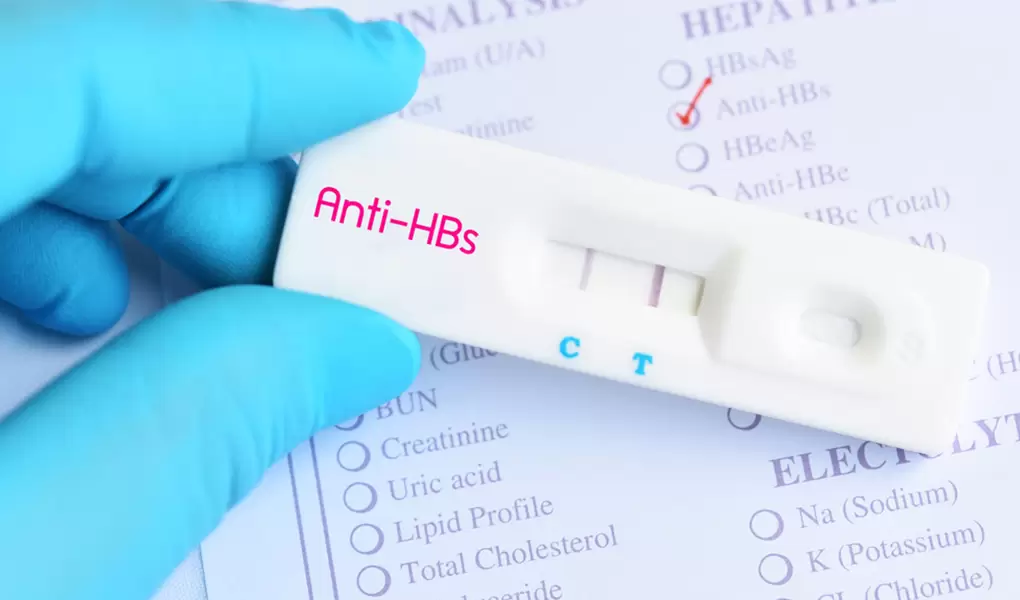
Laboratory testing plays a critical role in diagnosing hepatitis B and determining whether a person is infected, immune, or at risk. One of the most important blood markers used for this purpose is Anti-HBS. Understanding what Anti-HBS means and how to interpret positive or negative results is essential for evaluating immunity to hepatitis B.
Anti-HBS is a blood test that measures antibodies produced by the immune system against the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). These antibodies indicate whether the body has developed protection against the hepatitis B virus.
When a person is exposed to HBV or receives the hepatitis B vaccine, the immune system responds by producing antibodies. Anti-HBS antibodies bind to the surface antigen of the virus, preventing it from infecting liver cells. The presence of these antibodies generally indicates immunity.
The anti HBS test is therefore used to determine whether a person:
To fully understand Anti-HBS, it is important to distinguish it from other hepatitis B blood markers:
Anti-HBS alone does not reveal whether immunity developed due to vaccination or natural infection. For this distinction, the Anti-HBC test is required. A positive Anti-HBS with a negative Anti-HBC usually indicates vaccine-induced immunity.
A positive Anti-HBS result means that protective antibodies against hepatitis B are present in the blood. This indicates that the person is immune to the virus.
Many people ask “anti HBS positive means what?” or “what does anti HBS positive mean?” A positive result typically means one of the following:
Anti-HBS levels are measured in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL). In most laboratories:
If the Anti-HBS level is between 5 and 12 mIU/mL after vaccination, it may suggest that immunity is insufficient and a booster dose may be required.
An Anti-HBS negative result means that no protective antibodies against hepatitis B are detected in the blood. People often search for “anti HBS negative means” to understand this result.
A negative Anti-HBS test may indicate:
It is important to note that Anti-HBS negativity does not rule out active hepatitis B infection. To determine whether a person currently has hepatitis B, the HBsAg test must be evaluated.
Individuals with a negative Anti-HBS result are generally advised to receive the hepatitis B vaccine, especially if they are at increased risk of exposure.
The what is anti HBS test question is commonly asked by individuals reviewing their lab results. The Anti-HBS test is a blood test performed using immunological methods such as ELISA.
A blood sample is collected and analyzed to measure antibody levels. Results are typically available within one to two days. The test is used in several situations:
The test helps determine whether additional vaccination or medical follow-up is necessary.
Anti-HBS results are usually reported with a reference range. Interpretation depends on antibody concentration:
High Anti-HBS levels indicate that the immune system is prepared to neutralize the virus if exposure occurs.
The hepatitis B vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce Anti-HBS antibodies without causing infection. After completing the vaccination series, Anti-HBS testing may be performed to confirm immunity.
In some individuals, antibody levels may decline over time. This does not always mean that immunity is lost, but in certain cases, booster vaccination may be recommended.
Healthcare professionals often monitor Anti-HBS levels in people with occupational exposure risk.
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy or childbirth. For this reason, Anti-HBS testing is part of routine prenatal screening in many countries.
If a pregnant woman is Anti-HBS positive, it indicates immunity and reduces the risk of transmission. If Anti-HBS is negative, vaccination or further testing may be recommended to protect both mother and baby.
Some laboratory reports include results labeled as anti HBsAg positive means. This phrase generally refers to the presence of Anti-HBS antibodies against the hepatitis B surface antigen.
A positive Anti-HBsAg result confirms immunity rather than infection. It should not be confused with HBsAg positivity, which indicates active hepatitis B infection.
In most cases, Anti-HBS positivity indicates long-term or lifelong immunity. The immune system retains memory cells that can rapidly produce antibodies if the virus is encountered again.
Even if Anti-HBS levels decrease over time, immune memory often remains intact, providing continued protection.
Anti-HBS is an antibody that indicates immunity to hepatitis B.
Yes. Anti-HBS positivity means the person is protected against hepatitis B.
Yes. Recovery from natural hepatitis B infection also produces Anti-HBS antibodies.
Yes. Testing confirms whether the vaccine successfully produced immunity.
Anti-HBS itself does not cause liver cancer. Hepatitis B infection increases liver cancer risk, which is why immunity is important.
If you have any further questions about hepatitis B virus and anti-HBS test, you can contact us from 0090 216 444 39 49.
Let us call you as soon as possible regarding the issues you want to consult.