Follow Us!
Patient stories, informative videos and much more on our social media accounts

Having a healthy sperm count is one of the most important factors in male fertility. Sperm quality does not depend on a single parameter; it is evaluated based on sperm count, sperm motility, and sperm morphology. While genetic factors play a role, daily lifestyle habits—especially nutrition—have a significant impact on sperm production and overall reproductive health.
Scientific research shows that certain nutrients support hormone balance, protect sperm cells from oxidative stress, and improve sperm concentration and movement. For this reason, dietary choices are often recommended as a supportive approach for men who are planning to conceive naturally or undergoing fertility treatment.
Before examining foods that increase sperm count, it is helpful to understand how nutrition influences sperm production and which dietary habits may negatively affect sperm health.
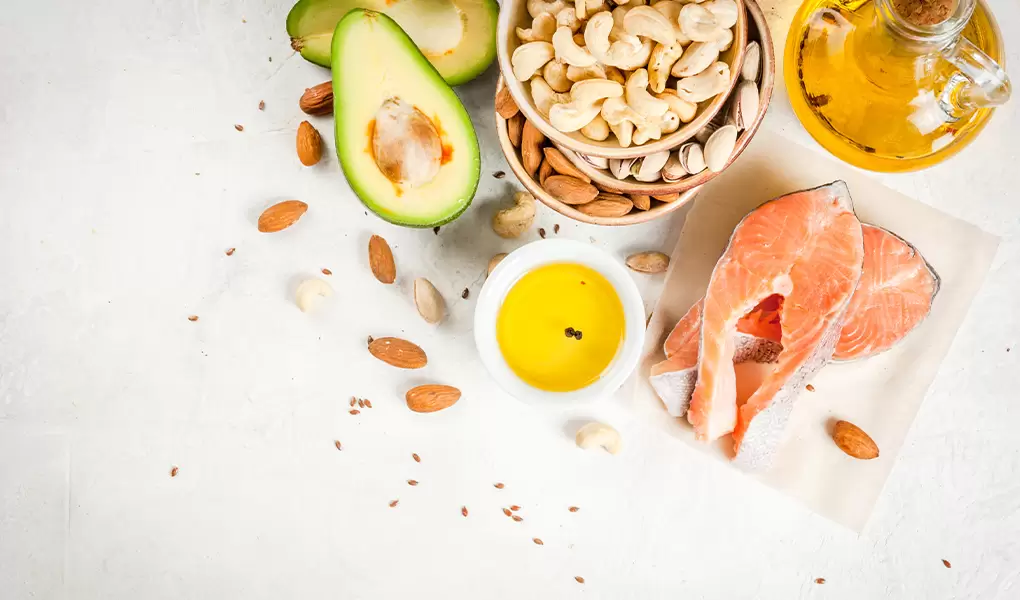
Foods that increase sperm count are generally rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients help protect sperm cells, support testosterone production, and improve sperm motility.
Seafood is among the most beneficial food groups for sperm health. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids play an essential role in sperm cell membrane structure and are associated with improved sperm count and motility.
Shellfish, particularly mussels and oysters, are rich in zinc. Zinc is critical for testosterone synthesis and normal sperm development. Studies indicate that men with low zinc levels are more likely to experience reduced sperm count.
Red and white meat provide high-quality protein, zinc, and iron, which are necessary for hormone production and tissue repair. These foods also contain coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a powerful antioxidant involved in cellular energy production.
Research suggests that CoQ10 may help improve sperm motility and concentration, especially in men with fertility problems. Balanced consumption of lean meat can therefore support sperm health.
Eggs are rich in vitamin B12, protein, and antioxidants. Vitamin B12 plays a key role in DNA synthesis and energy metabolism in sperm cells. Studies show that adequate B12 intake is associated with increased sperm count and improved sperm motility.
For this reason, eggs are often recommended as part of a fertility-supportive diet when consumed safely and in moderation.
Dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese are sources of vitamin D, calcium, and vitamin B12. Vitamin D has been linked to better sperm motility and hormonal balance. Men with sufficient vitamin D levels tend to show improved sperm parameters compared to those with deficiencies.
Low-fat dairy products are generally preferred to avoid excessive saturated fat intake.
Dark chocolate contains L-arginine, an amino acid involved in nitric oxide production. Nitric oxide supports blood flow and plays a role in sperm function. Some studies suggest that L-arginine intake may contribute to increased sperm count and motility.
Dark chocolate also contains antioxidants that protect sperm cells from oxidative stress, but it should be consumed in moderation.
Plant-based foods can also support sperm production, especially for men who follow vegetarian or vegan diets.
Green leafy vegetables such as spinach, lettuce, Brussels sprouts, and asparagus are rich in folate, a B vitamin essential for DNA synthesis. Low folate levels have been associated with reduced sperm concentration and abnormal sperm DNA.
These vegetables also provide vitamin C and other antioxidants that support sperm health.
Citrus fruits, strawberries, and melons are rich in vitamin C. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect sperm from oxidative damage. Studies have shown that increased vitamin C intake can improve sperm count, motility, and morphology.
Tomatoes contain lycopene, an antioxidant linked to improved sperm structure and activity. Regular consumption of tomatoes may help increase sperm concentration and motility.
Walnuts, hazelnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, and pumpkin seeds are beneficial for sperm health.
These foods provide:
Regular consumption has been associated with improved sperm count and motility.
Just as some foods support sperm health, others may negatively affect sperm production.
Foods and habits that may reduce sperm count include:
Alcohol consumption in particular has been associated with lower testosterone levels and impaired sperm production.
In some cases, dietary changes alone may not be sufficient. Hormonal treatments, such as injections containing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), may be prescribed for men with low testosterone levels.
These treatments are only suitable for selected patients and should be determined by a physician after blood tests and semen analysis.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, vitamin B12, folate, and antioxidants—such as fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and fruits—are associated with increased sperm count.
Eggs support sperm health due to their vitamin B12 content, but consuming raw eggs is not recommended because of infection risk.
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines are beneficial due to their omega-3 fatty acid content.
Yes. Walnuts and flax seeds contain omega-3 fatty acids that support sperm count, motility, and morphology.
Excessive alcohol, high soy intake, processed foods, and diets low in antioxidants may negatively affect sperm count.
Let us call you as soon as possible regarding the issues you want to consult.