Follow Us!
Patient stories, informative videos and much more on our social media accounts
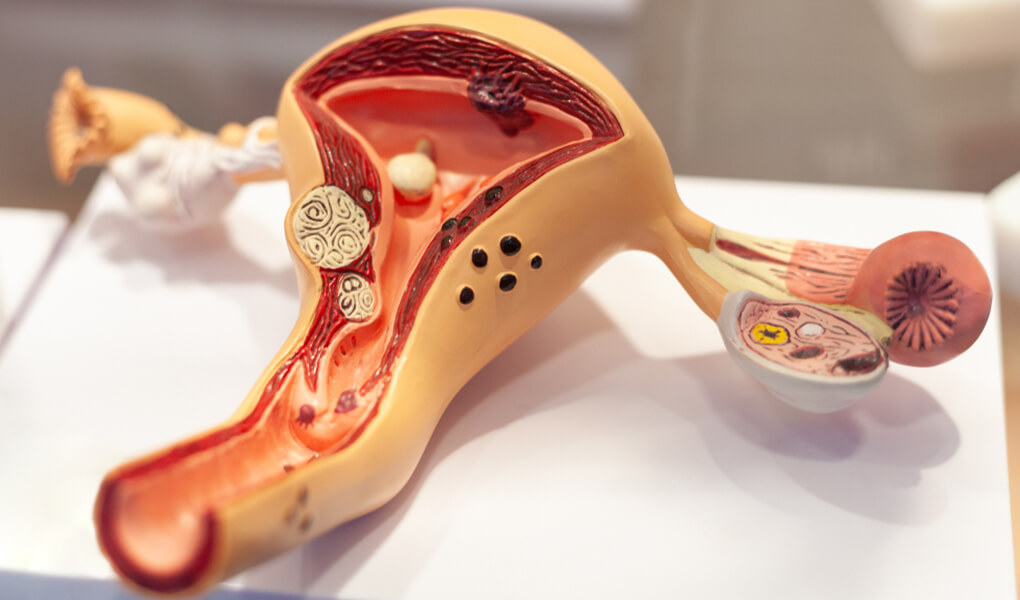
Uterine cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. According to World Health Organization (WHO) data, cancer remains a leading cause of death globally, and uterine cancer ranks among the most frequently diagnosed gynecologic cancers. In many countries, it is the fourth most common cancer in women.
Uterine cancer most commonly begins in the inner lining of the uterus (the endometrium) and is therefore often referred to as endometrial cancer. When detected early, uterine cancer is highly treatable and may be completely cured.
Uterine cancer develops when cells in the uterus grow uncontrollably and form a tumor. There are two main types:
Endometrial cancer accounts for the majority of uterine cancer cases.
The endometrium is the layer where a fertilized egg implants and pregnancy develops. During reproductive years, the hormones estrogen and progesterone regulate the monthly thickening and shedding of this lining.
Each month:
When there is prolonged exposure to estrogen without sufficient progesterone balance, the endometrial cells may begin to grow excessively. Over time, uncontrolled proliferation can lead to tumor formation.
If untreated, cancer may:
The exact cause of uterine cancer is not fully understood. However, hormonal imbalance, especially prolonged estrogen dominance, is believed to play a key role.
Increased risk is associated with:
The most common symptom of uterine cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Any vaginal bleeding after menopause is considered abnormal and should be evaluated immediately.
Other possible symptoms may include:
Symptoms may vary depending on the stage and whether the cancer has spread.
Get Free Expert SupportHaving one or more risk factors does not mean a woman will develop uterine cancer, but risk increases under certain conditions.
Most cases are diagnosed in women over 55. Risk increases with age.
Obesity increases the risk 2–4 times due to increased estrogen production from fat tissue.
Starting menstruation before age 12 increases lifetime estrogen exposure.
Menopause after age 50 extends estrogen exposure.
Hormone therapy without progesterone increases risk.
Chronic ovulation disorders increase estrogen exposure.
Especially multiple first-degree relatives with related cancers.
You should consult a doctor immediately if you experience:
Early diagnosis significantly improves treatment success.
Get Free Expert SupportTransvaginal ultrasound evaluates endometrial thickness and structure.
A thin tube is used to collect tissue from the uterine lining. This procedure usually does not require anesthesia.
If biopsy is insufficient, D&C may be performed under anesthesia to collect a larger sample.
Diagnosis is confirmed through pathological examination.
If cancer is confirmed, additional imaging and testing are performed to determine the stage.
Cancer confined to the uterus.
Cancer has spread to the cervix.
Spread to fallopian tubes, ovaries, vagina, or nearby lymph nodes.
Spread to bladder, colon, or distant organs such as lungs.
Treatment depends on:
Primary treatment. Hysterectomy (removal of uterus and cervix) is performed. Ovaries are often removed. Lymph nodes may also be removed.
Minimally invasive methods such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery may be used.
May be recommended after surgery to reduce recurrence risk or for patients unsuitable for surgery.
Typically used in advanced stages (Stage III–IV) or recurrence.
High-dose progesterone may be used in selected early-stage patients who wish to preserve fertility. Close monitoring is essential.
Complete prevention is not possible, but risk can be reduced by:
Obesity-related hormonal imbalance is one of the most significant modifiable risk factors.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially bleeding after menopause.
No. Uterine cancer usually refers to endometrial cancer, which starts in the lining of the uterus, while cervical cancer begins in the cervix.
Yes, especially when diagnosed early. Early-stage uterine cancer has a high treatment success rate.
No. Many women experience no pain in early stages. Abnormal bleeding is usually the first sign.
Women over 55, women with obesity, hormonal imbalance, PCOS, or prolonged estrogen exposure.
Growth rate varies depending on type. Endometrial cancer often progresses slowly and is detected early due to bleeding.
For any questions, you can contact us at 444 39 49.
Let us call you as soon as possible regarding the issues you want to consult.