Inability to conceive despite unprotected sexual intercourse for more than 1 year is called infertility. Infertiltiy can be sourced by women, men or it can be unexplained infertiltiy. By aging, women loose their fertility dramatically, therefore infertility cases are seen more often after a certain age on women patients. On the other hand, age does not impact on the fertility of men as much as women. Infertility, affects 15 – 20% of couples in Turkey.
Here are some factors that can cause male infertiltiy;
- Decrease in sperm count and movement
- Structural problems of sperm
- Absence of sperm cells in semen
- Undescended testicle at or after birth
- Channel obstructions
- Sperm not going out (emptying into the bladder)
- Febrile illnesses in childhood
- Adolescent diseases such as mumps
- Hormonal reasons
- Genetic diseases
- Varicocele: It is the enlargement of the veins leading to the testicle.
- Diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea
- Sexual dysfunction: Conditions such as erection problem or premature ejaculation
- Diabetes
- Previous cancer treatment
- Infections
- Testosterone deficiency
- Excessive smoking or alcohol consumption
- Stress
Here are some factors that can cause female infertiltiy;
- Destruction or congestion in tubes
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Ovulation disorders
- Reduced ovarian reserve
- Obstruction or adhesion of the fallopian (egg) tubes
- Previous infections or intra-abdominal operations
- Endometriosis: It is defined as the placement of the endometrium in the inner layer of the uterus and shedding every month as menstrual bleeding outside the uterus and affecting the function of the ovaries, uterus or fallopian tubes.
- High prolactin (milk hormone) level
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): In this syndrome, the body produces too much testosterone hormone, which affects ovulation.
- Polycystic
- Ovarian Syndrome is also associated with insulin resistance and obesity.
- Early menopause
- Uterine fibroids: These are benign tumors in the uterine wall.
- Intra-abdominal adhesions: Pelvic infection, appendicitis, adherent tissues formed after abdominal or pelvic surgery.
- Thyroid gland problems: Disorders in the thyroid gland (such as too little or too much thyroid hormone secretion) can affect the menstrual cycle and cause infertility.
- Cancer history and cancer treatment: Cancers that occur especially in the female reproductive system can lead to infertility.
- Radiotherapy and chemotherapy also affect a woman’s reproductive ability.
- Other medical conditions: Delayed puberty, inability to menstruate, liver disease, diabetes can also cause infertility in women.
- Excessive caffeine consumption
- Obesity
- Excessive smoking and alcohol consumption
Can You Understand Infertility Before Marriage?
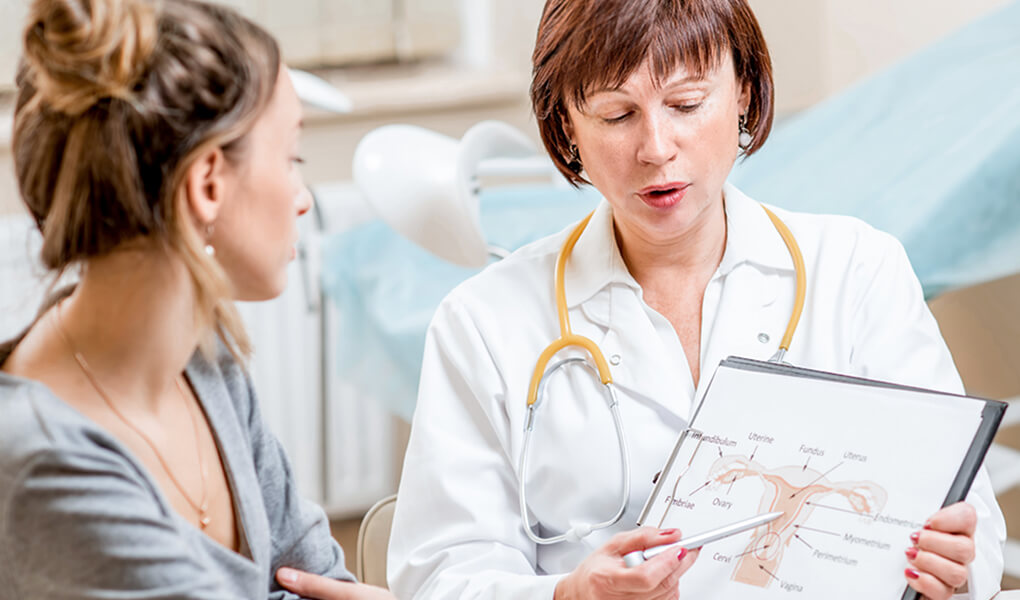
Especially before marriage, the question of how to understand infertility when single may come to mind. Although infertility is defined as not being able to conceive for more than 1 year, sexual intercourse is not necessary to diagnose infertility. Tests such as ultrasound imaging in women, measurement of hormone level in the blood to detect reproductive function disorders that may cause infertility; In men, tests such as sperm count and measurement of hormone level in the blood can be applied. Being single or married does not change the results of these tests. Therefore, it can be used easily for the diagnosis of infertility when single.
What Are Infertility Tests That Can Be Done Before Marriage?
The tests that can be done before and after marriage are the same for men. Being single does not require restriction of tests. However, there should be no vaginal intervention in the tests to be performed while waiting for women. For example, it is not appropriate to be performed before marriage because fluid is given into the uterus during intrauterine X-ray shooting.
Tests to measure sperm quality and hormone tests can be performed for male infertility. In women, hormone tests and extracorporeal ultrasonography can be performed while they are single.
Tests for Men
Infertility in men; can be detected by sperm count, motility and sperm structural disorder. At the same time, testosterone hormone and AMH level in the blood gives an idea about infertility.
In order to measure the sperm quality, sperm count is made by examining the sperm sample taken under a microscope after 3 to 5 days of sexual abstinence. Sperm count below 20 million / mL is called oligozoospermia and is a risk factor for infertility. In some patients, conditions such as azoospermia, that is, no sperm in the semen, are also encountered.
Blood tests can be done at any time to check the testosterone and AMH levels. As a result of the test, if the testosterone level is lower than 8-11 nmol / L or 300 ng / dL causes a decrease in sperm production. In addition, it causes infertility indirectly as it causes problems such as sexual anorexia and erectile dysfunction. AMH level is used to detect testicular functions and is a marker for infertility.
A simple physical examination by a doctor is sufficient to determine if there is a physical problem. More advanced methods include tests such as testicular biopsy, rectum and testicular ultrasound.
Tests for Women
In order to detect infertility in women, it is important to first recognize one’s own body. Irregularity in the menstrual cycle is considered a risk factor in terms of infertility. In addition, body temperature increases as a result of ovulation in the 2nd week of the menstrual cycle. By comparing the body temperature at these times with other days, you can have an idea about whether there is ovulation, but this method does not give a definite result. The delay in the first menstrual age is also an indication that there may be a hormonal problem in the body. It is very important for young girls who have not had their period at the age of 16 to have a medical examination, because the earlier hormonal disorders are diagnosed in women, the easier it is to treat.
Tests that do not require vaginal intervention are applied to diagnose infertility in women. Among these tests, there are methods such as checking estrogen, LH, FSH and AMH levels in the blood, and checking the state of the ovary and uterus by ultrasonography.
In the ultrasonography method, the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes are examined. These organs are checked for structural defects, obstructions, cysts and fibroids. In order to see the internal reproductive organs clearly in ultrasonography, the person to be ultrasound should be stuck in the urine. As a result of this extraction, problems such as obstruction, cyst, uterine fibroids are a risk factor in terms of infertility.
Blood should be drawn on the 2nd or 3rd day of the period in order to measure the hormone levels in the blood. Being married or single does not change the result of the hormone test, so it is an effective and reliable method for detecting single infertility. The hormones checked in this blood test and their meanings are as follows;
- AMH Test: Egg production in women occurs in the womb, new egg production is not made at the beginning of life, ie after birth. In other words, baby girls are born with a certain egg reserve and these eggs are used for life, and the reserve decreases with age. The amount of egg reserve is associated with infertility. AMH hormone test is a test that determines egg reserve. This test, which has been applied recently, shows the ovarian capacity much better than other hormone tests. As a result of the test, if the AMH level in the blood is below 1ng / mL, it can be said that the ovarian reserve is low.
- FSH: The FSH hormone provides the growth and development of the egg cell. FSH measurement is usually made within the first 5 days of the menstrual period and can provide information about ovarian reserves, albeit indirectly. When the level in the blood is over 12 mIU / mL, it can be interpreted as a problem in the ovarian reserve or that the ovaries are not healthy.
- LH: LH hormone, which rises in the middle of the menstrual period and provides ovulation, is also the main hormone that cracks the egg. LH / FSH ratio is greater than 1 at the beginning of menstruation. However, as LH production increases in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, the LH / FSH ratio may increase. If this rate is higher than 2.5, it raises suspicion of polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Prolactin: Normally, prolactin hormone, which is responsible for milk production after pregnancy, may increase regardless of any reason or due to the underactive thyroid glands. High prolactin hormone causes infertility.
- Testosterone: The testosterone hormone known as the male hormone increases in diseases such as polycystic ovary syndrome. It is recommended to check the testosterone level, especially in women with excessive hair growth problems.
You can contact us at 444 39 49 for all your questions.








Be the first to comment